What Is an STD Incubation Period?
The incubation period is how long it takes for an STD to show signs in your body after exposure. This isn’t the same as the “window period,” which is when an infection might not show up on a test yet, even if you have it.
Understanding incubation is crucial because:
- It affects testing accuracy: Testing too early can give false negatives.
- It affects symptom onset: Some infections flare up fast, others simmer quietly.
- It impacts sexual health decisions: Knowing when you're most infectious can prevent unknowingly spreading STDs.

People are also looking for: Can We Keep Up with Super-Gonorrhoea?
The Big Picture: STD Incubation Period Chart
Here’s a general breakdown of incubation periods for major STDs:
- Gonorrhea: 2–7 days
- Chlamydia: 1–3 weeks
- Syphilis: 10–90 days (usually ~3 weeks)
- Herpes (HSV-2): 2–12 days
- HIV: 2–6 weeks for acute symptoms
- HPV: 1 month to 6+ months
- Trichomoniasis: 5–28 days
- Hepatitis B: 6 weeks to 6 months
Source: CDC STD Screening Guidelines
Gonorrhea: The Fast-Mover
Incubation Period: 2–7 days
Common Symptoms:
- Burning urination
- Yellow/green discharge
- Pelvic or testicular pain
Gonorrhea comes on quick and loud, especially in people with penises. But in many vagina-owners, it stays quiet until complications like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) creep in.
Chlamydia: The Sneaky One
Incubation Period: 7–21 days
Common Symptoms:
- Burning when peeing
- Unusual vaginal/penile discharge
- Lower belly pain
Up to 70% of women and 50% of men never show symptoms, but can still transmit it. That’s why chlamydia gets dubbed the “silent spreader.”
Herpes (HSV-1 & HSV-2): The Latent Threat
Incubation Period: 2–12 days
Common Symptoms:
- Painful blisters or sores on the mouth, genitals, or anus
- Flu-like symptoms during first outbreak
Herpes doesn’t always play by the rules. Some people get blisters fast; others go months or even years before the first outbreak. The virus then hides in nerve cells and can reactivate.
Check Your STD Status in Minutes
Test at Home with RemediumGenital & Oral Herpes Test Kit

 For Men & Women
For Men & Women Results in Minutes
Results in Minutes No Lab Needed
No Lab Needed Private & Discreet
Private & DiscreetOrder Now $75.00 $98.00
For all 2 tests
Syphilis: The Slow Burn
Incubation Period: 10–90 days (typically around 21 days)
Common Symptoms:
- Painless sore (chancre) at the infection site
- Flu-like symptoms weeks later (fever, rash on palms/soles)
Syphilis is a master of disguise. That painless sore can appear and disappear without fanfare, leading people to miss the early warning. Left untreated, syphilis can move into serious neurological or cardiac stages months, or years, later.
HIV: The Invisible Spike
Incubation Period (for symptoms): 2–6 weeks after exposure
Common Symptoms of Acute HIV:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Sore throat or rash
- Swollen lymph nodes
These flu-like symptoms during the “acute phase” can be mistaken for a cold or COVID. But it’s when viral load is sky-high, and testing is tricky. Most HIV tests don’t detect the virus until 3–4 weeks after exposure.
A 2022 study in JAMA confirmed that early intervention significantly reduces transmission and long-term complications, even before full-blown symptoms appear.
HPV: The Long Game
Incubation Period: 1–8 months (can be longer)
Common Symptoms (when they appear):
- Genital warts (not painful, often soft or flesh-colored)
- Abnormal Pap smear results in people with cervixes
Most HPV infections resolve on their own, but high-risk strains can cause cervical, throat, or anal cancer. Unfortunately, there’s no test for HPV in men, and most don’t show symptoms.
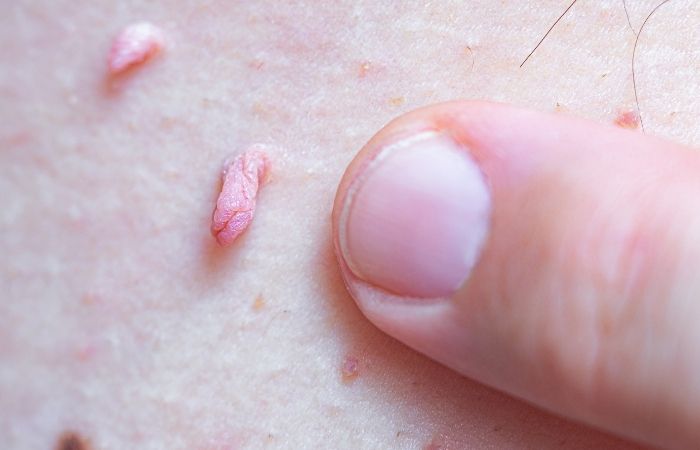
People are also looking for: The Fastest STDs to Show Up (And What to Watch For)
Trichomoniasis: The Underrated Irritant
Incubation Period: 5–28 days
Common Symptoms:
- Frothy, green-yellow discharge (in people with vaginas)
- Itching, burning, or redness
- Unusual odor
Trich is one of the most common, and least discussed, STDs. Many people dismiss it as a yeast infection or bacterial vaginosis, which delays diagnosis.
Hepatitis B: The Hidden Liver Threat
Incubation Period: 6 weeks to 6 months
Common Symptoms (if they appear):
- Fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Jaundice (yellow skin/eyes)
Hepatitis B is a virus that affects the liver and spreads through blood, sex, and shared needles. It’s often silent in the early stages, especially in adults, but can lead to chronic liver disease if not caught early.
Common Misconceptions About STD Incubation Periods
There’s a lot of confusion floating around STD timelines, especially online. Let’s bust a few myths.
Myth: If I don’t have symptoms, I’m not infected.
Truth: Many STDs are asymptomatic. No symptoms ≠ no infection.
Myth: You can test immediately after sex and get accurate results.
Truth: Most STDs need days or weeks to be detectable. Testing too early can lead to false reassurance.
Myth: You can only catch STDs from penetrative sex.
Truth: Oral, anal, and even skin-to-skin contact can transmit infections like herpes or HPV.
Check Your STD Status in Minutes
Test at Home with Remedium8-in-1 STD Test Kit

 For Men & Women
For Men & Women Results in Minutes
Results in Minutes No Lab Needed
No Lab Needed Private & Discreet
Private & DiscreetOrder Now $149.00 $392.00
For all 8 tests
Data Snapshot: What the Numbers Say
According to the CDC, over 26 million new STD infections occur each year in the U.S. alone. And nearly half happen in people aged 15–24. But get this: nearly 80% of those with chlamydia or gonorrhea don’t know they have it.
Testing trends also reveal something important: people often test too early. A 2023 review in Healthline found that premature testing leads to a significant number of missed diagnoses, especially for syphilis and HIV.
Real Talk: Anonymous Confessions
“I got tested a week after a hookup and thought I was fine. Then a month later, I tested positive for herpes. The first test was just too early.” Jordan, 31
“I had no idea chlamydia could show up three weeks later. I didn’t even have symptoms, but a routine test caught it. Honestly? I'm glad I didn't wait.” Samira, 24
These aren’t horror stories. They’re wake-up calls. Testing is care, not judgment.
FAQs
1. How soon do STD symptoms appear?
It depends on the STD, anywhere from 2 days (gonorrhea) to months (HPV or hepatitis B). Some never cause symptoms at all.
2. What’s the difference between incubation and window period?
Incubation is when symptoms show. Window period is when a test can detect the infection. They often overlap but aren’t the same.
3. Can I get an STD and show symptoms the next day?
Unlikely. Most STDs take at least 2–3 days to show symptoms, if they ever do. Fast symptoms usually mean another issue.
4. Do all STDs have symptoms?
No. Many (like chlamydia and HPV) are silent in the majority of cases. That’s why testing matters even without symptoms.
5. When is the best time to test after unprotected sex?
Wait at least 7 days for chlamydia/gonorrhea, 3 weeks for HIV, and 6 weeks+ for syphilis and hepatitis B for most accurate results.
6. Can STD symptoms come and go?
Yes. Herpes, in particular, flares and retreats. Other infections may briefly cause symptoms and then “go quiet.”
7. If I have discharge, is it definitely an STD?
No, but it’s a red flag. It could be a UTI or yeast infection, but it’s safest to rule out STDs with a test.
8. Is it possible to test negative but still have an STD?
Yes, especially if you test during the window period. Retest if symptoms continue or if you’re high risk.
9. Can you get an STD from oral sex?
Absolutely. Herpes, gonorrhea, and syphilis are all transmissible through oral contact.
10. How do I know if I need a combo test?
If you’ve had multiple partners, anonymous sex, or no symptoms but worry, a combo test kit is your best bet.
You Deserve Clarity, Not Shame
STD timelines are messy. Your body doesn’t follow a stopwatch, and symptoms don’t come with calendar invites. What matters is that you know your risk, get tested at the right time, and don’t panic if things feel off. Most STDs are treatable, many are curable. But timing your test is everything.
You’re not dirty. You’re not reckless. You’re a human being navigating intimacy, risk, and information. So be kind to yourself.
Sources
1. CDC STD Screening Recommendations
2. JAMA: Gonorrhea Incubation Review
3. Healthline: STD Incubation Q&A










