Quick Answer: White patches, bad breath, and swollen glands can be signs of an STD like oral gonorrhea, herpes, syphilis, or HIV, but they can also result from non-STD causes like thrush, strep throat, allergies, or smoking. The only way to know for sure is to get tested. Many oral STDs look like common conditions and are often misdiagnosed or missed entirely.
White Patches on Your Tongue or Tonsils
White patches in the mouth can mean a lot of things, from yeast infections (thrush) to autoimmune conditions to oral STDs like syphilis or gonorrhea. Location, texture, and timing matter.
STD-related causes include:
- Oral gonorrhea: White or yellow spots on tonsils, often mistaken for strep
- Syphilis: Flat, grayish-white mucous patches during secondary stage
- HIV: Chronic white lesions (oral hairy leukoplakia, thrush) from immune suppression
If patches don't scrape off or come with pain, fever, or swollen lymph nodes, STD testing is warranted.

People are also reading: The STD That Can Grow in Your Nose: When Syphilis Spreads Where You Least Expect
Persistent Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Bad breath isn’t always about brushing or garlic. When it lingers or worsens despite good hygiene, it may be linked to an infection, especially if accompanied by white patches or discharge.
Possible STD-related causes:
- Oral chlamydia or gonorrhea: Can cause pus or bacteria build-up in the throat
- HIV-related gingivitis: Chronic inflammation of the gums or tongue
- Syphilis: Late-stage ulcers or gummas can produce foul breath
Funky breath + throat discomfort = time to test.
Swollen Lymph Nodes: What’s That Lump in My Neck?
The lymph nodes under your jaw and in your neck help filter infections, but when they swell, it’s often a sign of viral or bacterial activity nearby. That includes STDs.
STD triggers for lymph node swelling:
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV): Often causes painful glands during outbreaks
- Syphilis: Swollen nodes during primary or secondary stages
- HIV: Persistent generalized lymphadenopathy is an early sign
If your gland is painful, large, or paired with a sore in your mouth, STD testing is crucial.
Oral Thrush vs. Oral Gonorrhea: How to Tell the Difference
Both thrush and gonorrhea can cause white tongue patches, soreness, and discomfort when swallowing. But they have different root causes and treatments.
Thrush: Yeast overgrowth, often in immunocompromised people, infants, or after antibiotics. White patches can be scraped off.
Oral gonorrhea: Bacterial STD; white or yellow coating on tonsils, hard to scrape off, may be accompanied by pus or fever.
If you’ve had oral sex recently and develop symptoms that don’t respond to antifungals, test for gonorrhea.
Tonsil Issues: White Dots or Swelling That Isn’t Strep
Not every sore throat is strep. In fact, many cases of tonsillitis caused by STDs go misdiagnosed because doctors don’t test for them in the mouth.
Gonorrhea and chlamydia can infect the tonsils, leading to:
- White spots or exudate
- Sore throat without cough
- Difficulty swallowing
Standard throat cultures don’t check for STDs unless you ask. If symptoms don’t improve or are recurring, get tested specifically for oral STDs.
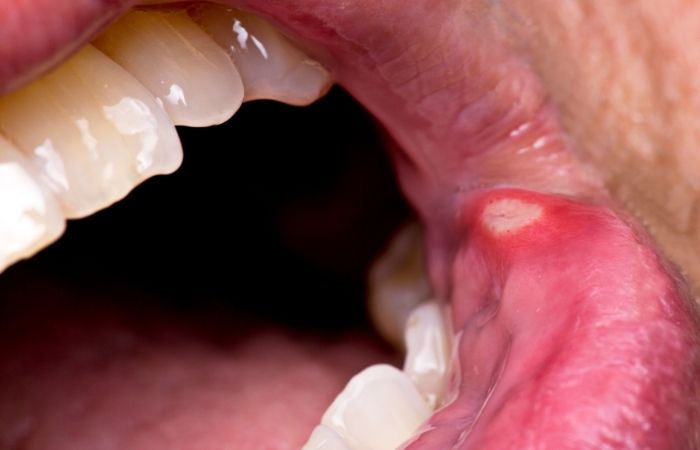
Herpes and Mouth Ulcers: More Than a Cold Sore
Most people associate herpes with lip blisters, but oral herpes can affect the inside of your mouth too. It often starts with tingling, followed by painful ulcers or fluid-filled blisters.
Oral herpes (HSV-1 or HSV-2) symptoms inside the mouth include:
- Shallow, painful ulcers on gums, tongue, or cheeks
- Crusting or bleeding sores
- Difficulty eating or brushing teeth
These aren’t just “canker sores”. Herpes ulcers often recur and cluster. Testing can confirm the virus even when active sores are gone.
Syphilis in the Mouth: When the Sore Isn’t Where You Expect
In primary syphilis, the first symptom is usually a painless sore (chancre), and yes, it can appear inside your mouth or on your lips if that’s where contact occurred.
Oral syphilis symptoms include:
- Single firm ulcer on tongue, lips, or inner cheek
- Gray-white mucous patches in secondary stage
- No pain but persistent swelling or lesion
These can be mistaken for apthous ulcers, cancer, or trauma. Blood testing is the only way to confirm syphilis, and the earlier the better.
Oral HPV: White Growths and Wart-Like Spots
HPV (human papillomavirus) isn’t always visible, but when it does show up in the mouth, it can look like:
- Cauliflower-like warts on the tongue or gums
- Flat white patches that don’t scrape off
- Lesions that slowly grow over weeks or months
HPV is linked to oral cancers, especially in the back of the throat and tonsils. Testing may involve biopsy, but in high-risk people, early HPV vaccination and monitoring is key.
HIV and Chronic Mouth Infections
HIV can manifest through persistent or recurrent mouth issues, particularly in the early or late stages of infection.
Common HIV-related oral symptoms include:
- Oral thrush (candida infection)
- Hairy leukoplakia (white “fuzzy” patches on the sides of the tongue)
- Chronic gum inflammation or ulcers
If you have more than one oral condition that won’t clear up, or frequent oral issues plus swollen glands, consider testing for HIV. Especially if you’ve had unprotected sex or recent STD exposure.
Other Causes That Aren’t STDs (But Still Matter)
Not every white patch or swollen node is an STD. Other possible causes include:
- Oral thrush: Yeast infection, especially after antibiotics
- Mononucleosis (mono): Sore throat, fatigue, and swollen tonsils with white patches
- Strep throat: Often causes white exudate and fever
- Smoking or chewing tobacco: Can cause white patches and increased cancer risk
- Vitamin deficiencies: B12 or iron deficiency can mimic infection symptoms
If symptoms persist longer than 7–10 days, testing is a good idea, especially if you’re sexually active.
Check Your STD Status in Minutes
Test at Home with Remedium8-in-1 STD Test Kit

 For Men & Women
For Men & Women Results in Minutes
Results in Minutes No Lab Needed
No Lab Needed Private & Discreet
Private & DiscreetOrder Now $149.00 $392.00
For all 8 tests
When to Suspect Oral STD Symptoms
Oral symptoms can be subtle or severe, but the following red flags should trigger STD suspicion:
- New or unusual mouth sores that don’t heal
- Persistent bad breath or strange taste in the mouth
- Swollen lymph nodes with no clear cause
- Discomfort during oral sex or swallowing
Trust your gut. If something feels “off” and you've had oral contact, get tested. Many oral STDs are curable or manageable, if caught early.
How Do Doctors Test for Oral STDs?
Testing for oral STDs often requires specific requests, regular throat swabs or blood work don’t always check for infections in the mouth. Here's what to expect:
Oral Gonorrhea/Chlamydia: Throat swab sent to a lab (NAAT test)
Herpes (HSV): Swab of active lesion or blood test for antibodies
Syphilis: Blood test (RPR or treponemal-specific)
HIV: Oral swab or blood test for antibodies and antigens
HPV: No standard test for oral HPV unless symptoms appear, biopsy may be required
Always tell your provider if your symptoms are oral and if you've had oral sex. Many providers won’t test unless you ask.
Can At-Home STD Tests Detect Oral Infections?
Yes, but with limitations. STD Rapid Test Kits offers accurate blood and urine-based tests for syphilis, HIV, herpes, chlamydia, and gonorrhea. However:
- Throat-specific infections like oral gonorrhea may be missed unless tested via swab
- Blood-based testing is still reliable for systemic infections (HIV, syphilis, HSV)
If your symptoms are mainly in your mouth or throat, consider combining at-home kits with a walk-in clinic throat swab for full coverage.
What If I’m Too Embarrassed to Talk About It?
You’re not alone. Many people feel ashamed bringing up mouth symptoms, especially if they’ve had unprotected oral sex or don’t know how to explain their concern without sounding “paranoid.”
Here’s how to get care discreetly:
- Use an at-home test kit for privacy and ease
- Write down your symptoms and give it to your provider if speaking is hard
- Ask for “oral STD testing” specifically, don’t rely on assumptions
You deserve answers, not judgment. Your mouth is just as valid a concern as any other body part.
People are also reading: Can HIV Show Up in Your Mouth? Early Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Can Oral STDs Spread to Other Parts of the Body?
Yes. Some STDs that start in the mouth can spread to the genitals or bloodstream if untreated. For example:
- Syphilis: Can become systemic and reach the nervous system
- HSV: Oral herpes can transmit to the genitals via oral sex
- HPV: Linked to oral and throat cancers if high-risk strains persist
Treating oral symptoms promptly helps protect your entire body, and your partners.
What Treatment Options Are Available for Oral STDs?
Once diagnosed, treatment depends on the specific infection:
- Gonorrhea/Chlamydia: Oral antibiotics (may require injection)
- Syphilis: Penicillin injection, often in stages
- Herpes: Antiviral medication (acyclovir, valacyclovir)
- HIV: Antiretroviral therapy (ART)
- HPV: No cure, but warts can be removed; vaccine prevents most strains
It’s important to finish your entire treatment course and notify recent partners if you test positive.
17. Should I Stop Kissing If I Have Oral Symptoms?
If you notice white patches, ulcers, or swollen glands, avoid kissing or oral contact until you know what’s going on. STDs like herpes, syphilis, and gonorrhea can spread through saliva or mucosal contact, even without full-blown sex.
Here’s when to pause mouth-to-mouth or oral contact:
- You have visible sores, white spots, or cuts in the mouth
- You’ve recently had unprotected oral sex and developed symptoms
- You’re waiting on test results or starting treatment for an oral STD
Kissing isn’t risk-free when symptoms are present. Take a break, get answers, and resume when you know it’s safe, for you and your partner.
Conclusion: Your Mouth Deserves the Same Attention as Your Genitals
We tend to treat the mouth as separate from the rest of our sexual health, but that’s a dangerous myth. Oral sex is sex. And your tongue, throat, and tonsils are all vulnerable to infection, whether you had symptoms last week or just noticed a lump this morning.
White patches, weird breath, swollen glands, none of these are “just in your head.” They might be harmless, or they might be signs of a hidden STD. Either way, you have every right to know what’s going on inside your body.
Don’t wait until it gets worse. STD Rapid Test Kits offers discreet, accurate testing that lets you take action fast, without judgment, appointments, or waiting rooms. Your mouth is part of your sex life. It deserves the same protection.
Check Your STD Status in Minutes
Test at Home with Remedium10-in-1 STD Test Kit

 For Women
For Women Results in Minutes
Results in Minutes No Lab Needed
No Lab Needed Private & Discreet
Private & DiscreetOrder Now $189.00 $490.00
For all 10 tests
FAQs
1. Can white patches on my tongue mean an STD?
Yes. Oral gonorrhea, syphilis, and HIV-related conditions like thrush or leukoplakia can all cause white patches.
2. What STDs cause bad breath?
Oral gonorrhea, HIV-related gum infections, and late-stage syphilis can lead to halitosis. Chronic bad breath may signal infection.
3. Are swollen neck glands an STD symptom?
Yes. Herpes, syphilis, and HIV often trigger swollen lymph nodes near the jaw or throat, especially during early stages.
4. Can I get gonorrhea in my throat?
Absolutely. Oral sex can transmit gonorrhea to the throat. Many cases are asymptomatic or mimic sore throat and strep.
5. Will an at-home STD test work for oral infections?
Yes and no. Blood-based infections like syphilis or HIV can be detected. For oral gonorrhea/chlamydia, a throat swab is better.
6. What’s the difference between oral thrush and gonorrhea?
Thrush is a yeast infection, often white and easily scraped. Gonorrhea causes yellow or white spots on tonsils, harder to remove, and more painful.
7. Should I test if I only had oral sex?
Yes. Oral sex can transmit STDs including gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, HPV, and HIV. Testing is smart even without symptoms.
8. What if I’m embarrassed to talk about my mouth symptoms?
You can use an at-home test for privacy or write your symptoms down for your provider. You’re not alone, millions face this.
9. How long should I wait before testing after oral sex?
Most oral STDs show up within 1–2 weeks. Syphilis may take longer. Test sooner if symptoms appear quickly.
10. Can STD symptoms go away on their own?
Sometimes, but the infection may still be active. Always test and treat to avoid complications or transmission.
Sources
1. What causes white spots on your throat – Healthline (strep throat, thrush, mono, herpes)