Syphilis Retesting After Treatment: How Long Should You Wait?
The Historical Debate Over Syphilis's Origins
Historians and medical researchers have some different opinions on the place of the very first outbreak of syphilis. There are two main hypotheses:
- Most Europeans adopt the Columbian Theory that suggests Christopher Columbus and his crew brought syphilis back from the Americas upon their return in 1493. Proponents of this theory argue that skeletons of Native Americans found prior to the arrival of Columbus showed evidence of treponemal infections, a class of bacteria responsible for syphilis.
- Some researchers claim that syphilis was present in Europe even before Columbus's arrival. They refer to the signs of the same symptoms from medieval literature and the skeletal remains as proof. This theory has been termed the pre-Columbian theory. According to this view, a more dangerous form of the disease cropped up in the late 1500s.
Syphilis was first recorded in 1495 among French soldiers who were fighting in the Italian Wars. Its true origin is unknown but from this, it came to be known as the "French Disease."
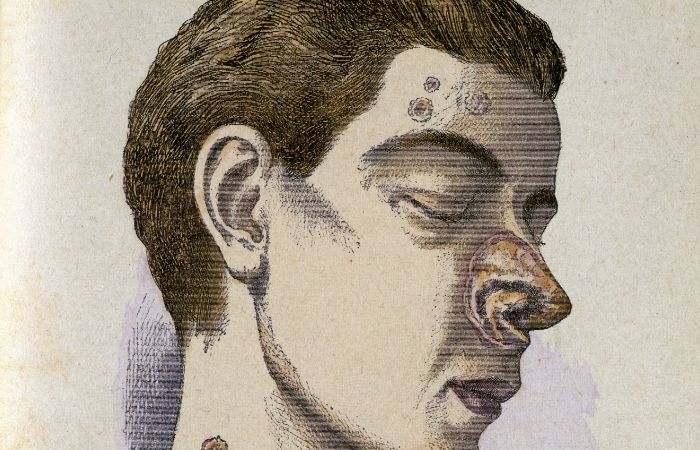
Syphilis: How It Spreads and Early Treatments
The introduction of syphilis into Europe helped in its quick spread around the globe. Isolated reports of cases were mentioned in the 16th century in the Middle East, Africa, and even Asia. Treatments in the early stages were crude and did more harm. They included:
- Mercury treatments: Highly toxic to the patients subjected to mercury fumes or mercury-containing ointment.
- Guaiac wood: Also called holy wood, this resinous wood from trees of the Americas was supposed to have curative powers.
- Sudation Treatment: A treatment in which patients lay under blankets or in steam rooms in order to "sweat out" the disorder.
Because these remedies did little more than cover symptoms, the old adage ran: "A night with Venus, a lifetime with Mercury."
Order Now $33.99 $49.00 Check Your STD Status in Minutes
Test at Home with Remedium
Syphilis Test Kit




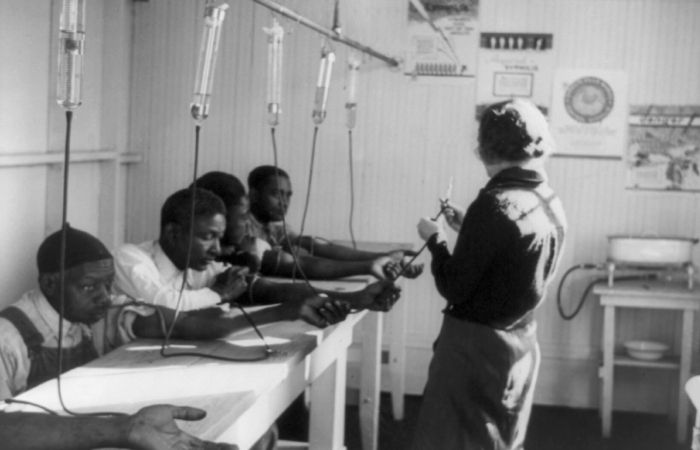
The Tuskegee Syphilis Study: A Grim Chapter in Medical History
The Tuskegee Syphilis Study, despite being very controversial, marked a turning point from 1932 to 1972 in the history of syphilis. The United States Public Health Service conducted an experiment whereby they observed responses of African American men to syphilis over a certain period of time, pretending to offer them free health care while withholding medication even after penicillin became largely available in the 1940s.
This unethical study resulted in general loss of confidence in the system and called for improvement in the ethics of research, including requirements for informed consent and stricter laws to protect human subjects.

Penicillin Discovery
The 1928 discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming significantly changed the way in which syphilis would be treated. Penicillin became the most common antibiotic in service during the 1940s and replaced the more dangerous other therapies. The number of deaths caused by syphilis declined because of this discovery, leading to:
- A decline in congenital syphilis, a disease resultant from mother-child transmission.
- More public education programs emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Even with the advances in recent times, syphilis is considered a public health concern because of periodic outbreaks recorded from various parts of the world.
Syphilis and Modern Medicine: Treatments and Challenges
Diagnosis of syphilis infection is through blood tests, and treatment involves the administration of penicillin injection. However, the following concerns still need to be addressed:
- Resurgence of Syphilis: The incidence of syphilis, particularly among the high-risk population, has shown a resurgence in recent times.
- Antibiotic Resistance: Antibiotic resistance, though still usually treatable, is watched closely by researchers for signs of resistance.
- Delayed Treatment: Due to the insidious nature of this disease, many people are sick yet don’t feel it and therefore put off treatment.
- Prevention Efforts: Public health centers emphasize safe sexual behaviors and frequent testing for sexually transmitted infections as methods to prevent syphilis.
Order Now $69.00 $147.00 Check Your STD Status in Minutes
Test at Home with Remedium
3-in-1 STD Test Kit




For all 3 tests
Syphilis and Its Impact on Health and Medicine
The effects of syphilis have extended to most aspects of civilization, including:
- The Arts: Syphilis has been expressed in literature and the arts through the works of painters such as Edvard Munch and poets such as William Shakespeare.
- Medical and Epidemiology Advancements: Due to syphilis, researchers have gained new knowledge in the biological field of study, epidemiology, and antibiotics.
- Public Health Policies: Governments worldwide have introduced policies such as free treatment services, education, and testing.
Syphilis: Myths and Facts
Yet another myth is spread about syphilis. Let’s straighten things out:
- "Syphilis is an infection that no longer exists." That is not true. Infection rates are on the rise.
- "Only people who are promiscuous acquire syphilis." That is not true. Syphilis can be found among many types of people.
- "Condoms totally prevent syphilis." That is not true. Even with condoms, syphilis can be spread through contact with infected lesions.

FAQs
1.- What are the symptoms of syphilis?
Chancres, rashes, and flu-like symptoms all of which are painless.
2.- How long after infection do symptoms appear?
Blood tests or microscopic examination of lesions.
3.- Will syphilis ever be cured?
Yes, the moment penicillin is administered.
4.- Can somebody get syphilis again if he or she has been treated for the infection?
Yes, a second infection can occur once one exposes him or herself once more to syphilis infection.
5.- What happens if syphilis is left untreated?
Some of the most serious complications include blindness, organ failure, and neurological problems.
6.- Can syphilis be transmitted to the fetus during pregnancy?
Yes, congenital syphilis can lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, or birth defects.
7.- How prevalent is syphilis?
In recent years, it has gained ground in a number of countries among certain groups of the population.
8.- Is it possible to get syphilis via kissing?
That's relatively rare, but this could be the case if you have sores in your mouth because of syphilis.
9.- Can I test myself for syphilis at home?
Yes, you can purchase a home test kit that will provide you with private, accurate results.
10.- More information about sexually transmitted diseases such as syphilis
Check out our blog for well-informed articles on different STDs, their prevention, and means of testing.
The Need to Test
The historical path of the syphilis pandemic serves as a lesson about the importance of public health programs, ethical research, and medical development. Syphilis has had a profound impact on human history, although it is now curable.
If you think you may have been exposed to a sexually transmitted disease, you can use an at-home test kit to get a private and accurate result. For the most current information, please check out our blog on syphilis and other sexually transmitted illnesses.
Sources
1.- History of Syphilis Part 1
3.- Clinical Infectious Diseases: Syphilis Research
4.- ScienceDirect: Syphilis Studies